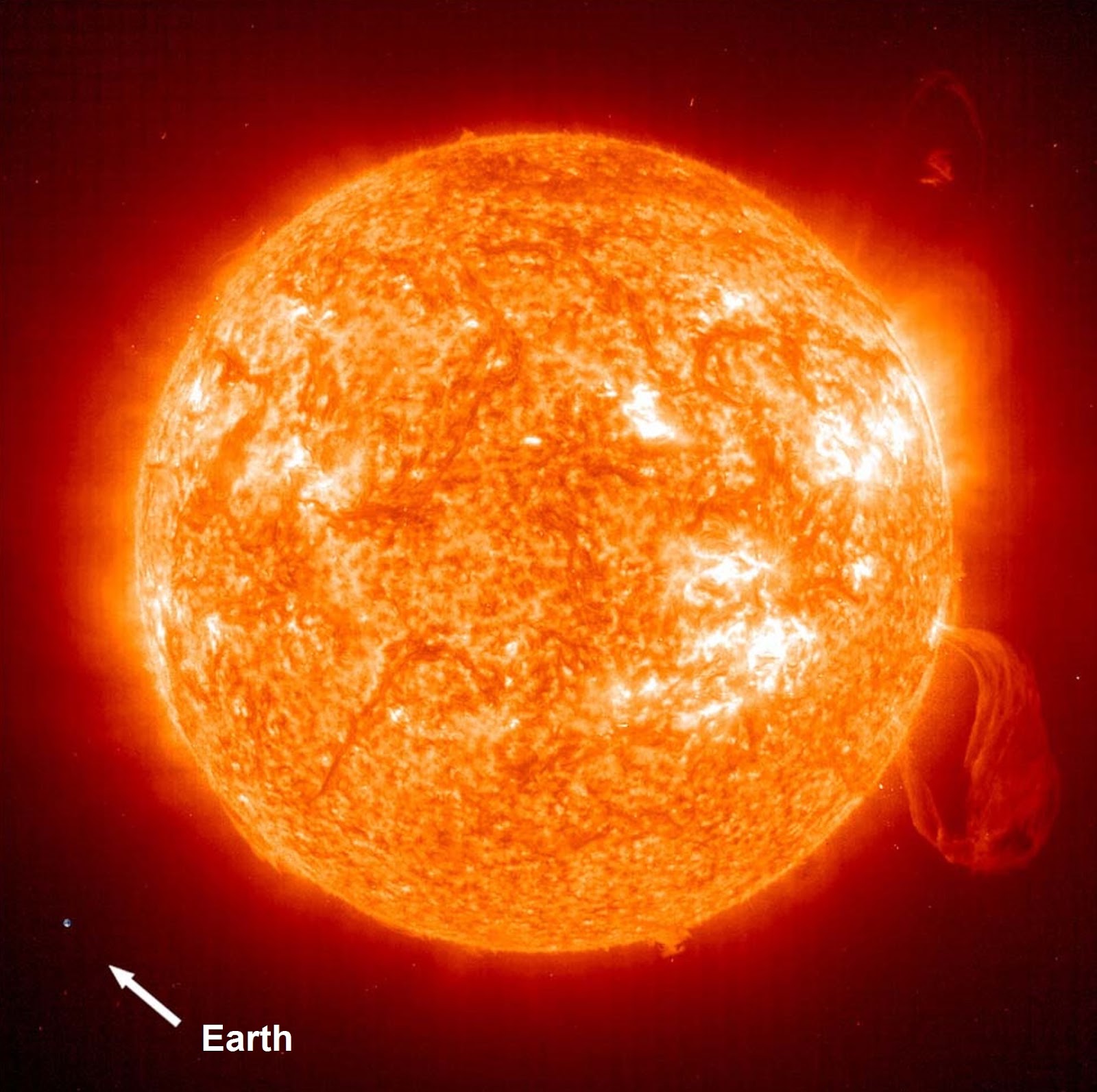
Have you ever wondered about the sheer size of the Sun compared to Earth? The vastness of space often leads us to ponder the dimensions of celestial bodies, particularly those within our solar system. The Sun, our closest star, is a colossal sphere of hot plasma and energy, while Earth is our familiar blue planet teeming with life. Comparing their sizes offers a fascinating glimpse into the scale of the universe and the forces that govern our cosmic neighborhood.
The Earth and the Sun are two vastly different celestial entities, both in terms of size and function. The Sun's diameter is approximately 109 times that of Earth, making it a gigantic ball of fire in the sky. This comparison not only highlights the Sun's immense size but also its critical role in the solar system. It is the gravitational anchor for the planets, and its light and heat sustain life on Earth. Understanding the Earth-Sun size comparison helps us appreciate the delicate balance that allows life to thrive on our planet.
In this article, we will delve deep into the "earth sun comparison size," exploring various aspects of these celestial bodies and their impact on each other. From their physical dimensions and compositions to their influences on life and climate, we will cover every facet of this intriguing subject. So, buckle up as we embark on a journey to understand the vast differences and mesmerizing similarities between Earth and its closest star, the Sun.
Table of Contents
- What is the Earth-Sun Size Comparison?
- Understanding the Sun: The Solar Giant
- The Earth's Dimensions: Our Home Planet
- How Does the Sun's Size Affect Earth?
- Earth and Sun Composition: What's Inside?
- Solar Influence on Earth's Climate
- Gravitational Forces Between Earth and Sun
- Solar Energy and Life on Earth
- The Sun's Role in the Solar System
- Technological Applications of Solar Knowledge
- Future Exploration of the Sun and Earth
- What are the Unknowns in Earth-Sun Comparison?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion: The Cosmic Dance of Earth and Sun
What is the Earth-Sun Size Comparison?
The "earth sun comparison size" is a fascinating topic that underscores the vastness of our universe. At the core of this comparison is the realization that the Sun is enormous compared to Earth. The Sun's diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers, while Earth’s diameter is just 12,742 kilometers. This means that you could line up approximately 109 Earths across the face of the Sun.
This comparison isn't just about numbers; it provides insight into the scale and interactions within our solar system. The Sun's massive size contributes to its gravitational pull, which keeps all the planets, including Earth, in their orbits. Without the Sun's size and gravitational force, the solar system as we know it would not exist.
Moreover, the Sun comprises 99.86% of the solar system's total mass, which shows its dominance in terms of size and gravitational influence. Understanding this comparison helps us grasp the importance of the Sun in our daily lives and its impact on Earth's climate and ecosystems.
Understanding the Sun: The Solar Giant
The Sun is a star at the center of our solar system, and its size is a defining feature. Composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, the Sun is a massive sphere of hot plasma. Its core is where nuclear fusion occurs, producing the energy that powers the Sun and provides light and heat to the planets orbiting it.
The Sun's enormous size means it has a powerful gravitational force. This force is what keeps the planets in orbit around the Sun. The Sun's gravity is 28 times that of Earth's, which explains why it can hold such a vast system of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in place.
Another aspect of the Sun's size is its surface temperature, which is around 5,500 degrees Celsius. This intense heat is a result of the nuclear reactions taking place in its core, where temperatures can reach up to 15 million degrees Celsius. The energy produced by these reactions is emitted as sunlight, which sustains life on Earth.
The Earth's Dimensions: Our Home Planet
Earth, as our home planet, is the largest of the terrestrial planets in the solar system. With a diameter of 12,742 kilometers, Earth is a fraction of the Sun's size. However, its size is perfect for sustaining life. Earth's mass and gravity are sufficient to maintain an atmosphere and provide the right conditions for water to exist in all three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
Earth's size is also crucial for its geologic activity. The planet's core is hot and active, driving the movement of tectonic plates. This activity leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions, all of which play a role in shaping Earth's surface and climate.
Despite its smaller size compared to the Sun, Earth is a complex and dynamic planet. Its size allows it to have a diverse range of ecosystems and climates, supporting a wide variety of life forms. Understanding Earth's dimensions in comparison to the Sun helps us appreciate the delicate balance that enables life to thrive here.
How Does the Sun's Size Affect Earth?
The size of the Sun has a profound impact on Earth and its environment. One of the most significant effects is the gravitational pull the Sun exerts on Earth, which keeps it in a stable orbit. This orbit is critical for maintaining the conditions necessary for life, including a stable climate and the cycle of day and night.
The Sun's size also affects the amount of solar radiation that reaches Earth. This radiation is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce energy and oxygen. Without the Sun's light and heat, Earth would be a cold, lifeless planet.
Moreover, the Sun's size and energy output influence Earth's climate. Solar radiation drives weather patterns and ocean currents, affecting everything from global temperatures to precipitation. Changes in the Sun's activity, such as solar flares and sunspots, can also impact Earth's climate and technological systems.
Earth and Sun Composition: What's Inside?
Understanding the composition of Earth and the Sun provides insight into their differences and similarities. The Sun is primarily composed of hydrogen (about 74%) and helium (about 24%), with trace amounts of other elements. These elements undergo nuclear fusion in the Sun's core, producing the energy that powers the solar system.
In contrast, Earth is composed of a variety of elements, with iron, oxygen, silicon, and magnesium being the most abundant. Earth's composition is layered, with a solid inner core, a liquid outer core, a mantle, and a crust. This layered structure is responsible for Earth's magnetic field and tectonic activity.
The differences in composition between Earth and the Sun highlight their distinct roles in the solar system. While the Sun is a source of energy and light, Earth is a habitable planet with a complex structure that supports life.
Solar Influence on Earth's Climate
The Sun plays a crucial role in Earth's climate system. Solar radiation is the primary source of energy for Earth's climate, driving atmospheric circulation and ocean currents. This energy is absorbed by Earth's surface and atmosphere, warming the planet and regulating its climate.
Changes in solar activity can have significant impacts on Earth's climate. For example, periods of increased solar activity, such as solar maxima, can lead to warmer global temperatures. Conversely, periods of decreased solar activity, such as solar minima, can result in cooler temperatures.
The Sun's influence on Earth's climate is also evident in the phenomenon of solar cycles, which are approximately 11-year cycles of solar activity. These cycles can affect weather patterns, climate variability, and even human activities, such as agriculture and energy consumption.
Gravitational Forces Between Earth and Sun
The gravitational forces between Earth and the Sun are fundamental to the stability of the solar system. The Sun's gravity is the dominant force that holds the planets in their orbits, including Earth. This gravitational pull ensures that Earth remains at a stable distance from the Sun, allowing for a habitable climate.
Earth's gravity also plays a role in the interaction between the two celestial bodies. The gravitational force between Earth and the Sun is responsible for the phenomenon of tides, which are caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and the Moon on Earth's oceans.
Understanding the gravitational forces between Earth and the Sun is crucial for studying the dynamics of the solar system and predicting celestial events, such as eclipses and planetary alignments.
Solar Energy and Life on Earth
Solar energy is vital for life on Earth. It provides the heat and light necessary for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. This energy is then transferred through the food chain, supporting all life forms on Earth.
The Sun's energy also drives the water cycle, which is essential for maintaining Earth's ecosystems. Solar radiation causes water to evaporate from the surface of oceans and other bodies of water, forming clouds and precipitation. This cycle is crucial for providing fresh water to Earth's inhabitants.
In addition to supporting life, solar energy has numerous technological applications. Solar panels, for example, harness the Sun's energy to generate electricity, providing a renewable and sustainable source of power for homes and businesses.
The Sun's Role in the Solar System
The Sun is the central figure in the solar system, playing a vital role in its structure and dynamics. As the largest and most massive object in the solar system, the Sun's gravity holds the planets, moons, and other celestial bodies in their orbits.
The Sun's energy output, known as solar radiation, is crucial for maintaining the temperature and climate of the planets. This energy drives the weather patterns and climate systems of planets like Earth, supporting life and influencing geological processes.
In addition to its gravitational and energy roles, the Sun is also the source of solar wind, a stream of charged particles that flow from the Sun's atmosphere into space. This solar wind interacts with planetary magnetic fields, creating phenomena such as auroras and influencing space weather.
Technological Applications of Solar Knowledge
Understanding the Sun and its interactions with Earth has led to numerous technological advancements. Solar energy, for example, has become a significant source of renewable energy, with solar panels and solar farms harnessing the Sun's power to generate electricity.
In addition to energy production, knowledge of the Sun has applications in space exploration and telecommunications. Satellites, for example, rely on solar panels to generate power and maintain communication with Earth. Understanding solar activity is also crucial for protecting satellites and other space-based technologies from solar storms and radiation.
Furthermore, studying the Sun and its interactions with Earth has led to advancements in climate science and meteorology. By understanding the Sun's role in Earth's climate system, scientists can better predict weather patterns and climate variability, improving our ability to respond to natural disasters and climate change.
Future Exploration of the Sun and Earth
Future exploration of the Sun and Earth will continue to provide valuable insights into their interactions and the dynamics of the solar system. Missions such as NASA's Parker Solar Probe and the European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter are designed to study the Sun's atmosphere and solar wind, providing new data on the Sun's behavior and its impact on the solar system.
On Earth, advancements in technology and scientific research will continue to improve our understanding of Earth's climate and ecosystems. Satellite observations, for example, provide valuable data on Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land, helping scientists monitor changes and predict future trends.
Future exploration of the Sun and Earth will also have implications for space exploration and the search for extraterrestrial life. Understanding the Sun's behavior and its influence on planetary climates will be crucial for identifying habitable environments beyond our solar system.
What are the Unknowns in Earth-Sun Comparison?
Despite our extensive knowledge of the Earth-Sun comparison, there are still many unknowns and areas for further research. One of the primary challenges is understanding the complex interactions between the Sun's activity and Earth's climate. While we know that solar activity can influence climate patterns, the precise mechanisms and long-term effects are still being studied.
Another area of uncertainty is the role of the Sun in driving climate change. While human activities are the primary cause of recent climate change, understanding the Sun's natural variability and its influence on Earth's climate is crucial for accurately predicting future climate scenarios.
Additionally, the Sun's internal processes, such as nuclear fusion and magnetic field dynamics, are still not fully understood. Continued research and exploration are necessary to uncover these mysteries and improve our understanding of the Sun and its role in the solar system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many Earths can fit inside the Sun?
Approximately 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the Sun, highlighting the vast difference in their sizes.
Why is the Sun so much larger than Earth?
The Sun's size is due to its composition and the processes of nuclear fusion that take place in its core, which generate immense energy and mass.
What is the impact of the Sun's size on Earth's orbit?
The Sun's size and gravitational pull keep Earth in a stable orbit, which is crucial for maintaining a habitable climate and the cycle of day and night.
Does the Sun's size affect Earth's climate?
Yes, the Sun's size and energy output influence Earth's climate by driving weather patterns and ocean currents, affecting global temperatures and precipitation.
What role does the Sun play in supporting life on Earth?
The Sun provides the heat and light necessary for photosynthesis, which supports the food chain and drives the water cycle, essential for sustaining life.
How does the Sun's energy benefit technology on Earth?
The Sun's energy is harnessed through solar panels to generate electricity, providing a renewable and sustainable source of power for homes and businesses.
Conclusion: The Cosmic Dance of Earth and Sun
The "earth sun comparison size" is a captivating topic that underscores the vastness and complexity of our solar system. The Sun's massive size and energy output are fundamental to the stability and dynamics of the solar system, influencing Earth's orbit, climate, and life. Understanding the differences and similarities between Earth and the Sun helps us appreciate the delicate balance that allows life to thrive on our planet.
As we continue to explore and study the Sun and Earth, we will uncover new insights into their interactions and the forces that govern our cosmic neighborhood. This knowledge will not only enhance our understanding of the solar system but also inform our efforts to address global challenges, such as climate change and sustainable energy.
In conclusion, the Earth-Sun comparison is a reminder of the interconnectedness of all celestial bodies and the intricate dance that shapes our universe. By studying this cosmic relationship, we gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the cosmos and our place within it.
You Might Also Like
Discover The Future: Mars Aspects 2025's Impact On Space ExplorationUnderstanding Trigonal Pyramidal Angle: A Comprehensive Guide
Anticipating The Release Of Ibomma New Movie 2025: A Cinematic Marvel
Ecchi Anime: Meaning, Origins, And Cultural Impact
Gemini And Sagittarius: A Cosmic Connection Unveiled
Article Recommendations